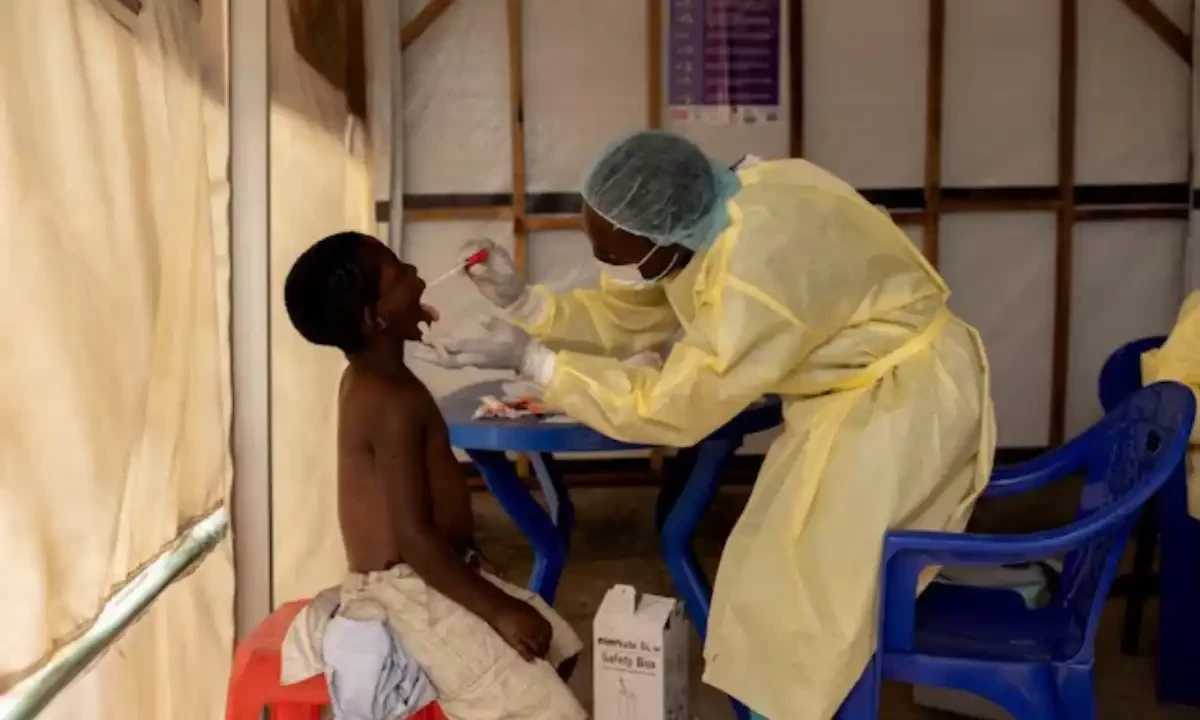
The World Health Organization (WHO) has declared the mpox outbreak in parts of Africa a public health emergency of international concern.
The outbreak, which began in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), has claimed at least 450 lives and has spread across central and east Africa.
WHO’s chief warned about the potential spread of the disease in the region and beyond.
Mpox, The Monkeypox
Mpox, formerly known as monkeypox, is a highly contagious disease transmitted through close contact, including skin-to-skin contact, sexual activity, and close proximity when talking or breathing.
It causes flu-like symptoms and skin lesions and can be fatal, with an estimated death rate of 4% for those infected.
Vaccines can help prevent infections, but they are reserved for serious patients in case they are near dying.
Since the beginning of 2024, more than 13,700 cases have been reported in the DRC, with the disease also detected in Burundi, the Central African Republic, Kenya, and Rwanda.