If you’ve been following the astronomy community on the internet you’ve likely come across a story about the James Webb Space Telescope’s latest find: The “oldest galaxy we’ve ever seen”. Yes, just a week after its first images were shown to the world, the James Webb Space Telescope may have found a galaxy that existed 13.5 billion years ago, a scientist who analyzed the data said Wednesday.
What’s The Galaxy Been Called And How Old Is It?
🚨 JWST has potentially smashed records, spotting a galaxy which existed when the universe was a mere 300 million years old! The light from GLASS-z13 took 13.4 billion years to hit us, but the distance between us is now 33 billion light years due to the expansion of the universe! pic.twitter.com/5AcOBwHuO1
— Dr. James O'Donoghue (@physicsJ) July 20, 2022
Known as GLASS-z13, the galaxy dates back to 300 million years after the Big Bang, about 100 million years earlier than anything previously identified, Rohan Naidu of the Harvard Center for Astrophysics said.
“We’re potentially looking at the most distant starlight that anyone has ever seen,” he said.
How JWST Captured The Galaxy And How Does It Look Like?
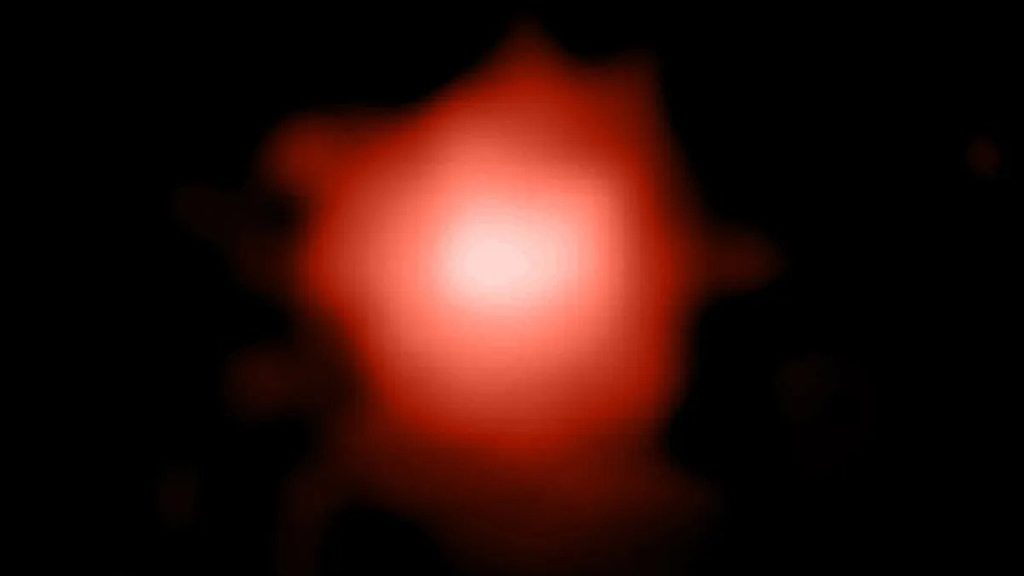

GLASS-z13 was spotted in so-called “early release” data from the orbiting observatory’s main infrared imager, called NIRcam and when translated from infrared into the visible spectrum, the galaxy appears as a blob of red with white in its center, as part of a wider image of the distant cosmos called a “deep field”.
Why Is It So Hard To Capture Such Distant Objects And How JWST Is The Only Solution?
Such Objects are so distant from Earth that by the time their light reaches us, it has been stretched by the expansion of the Universe and shifted to the infrared region of the light spectrum. And JWST is the only satellite that has been built with such scenarios in mind.
Which Galaxy Was The Previous Record Holder?
The previous oldest identified galaxy, found by the Hubble Space Telescope, is called GN-z11 and dates back to 400 million years after the birth of the universe. It was born 100 million years earlier than the one discovered by JWST.